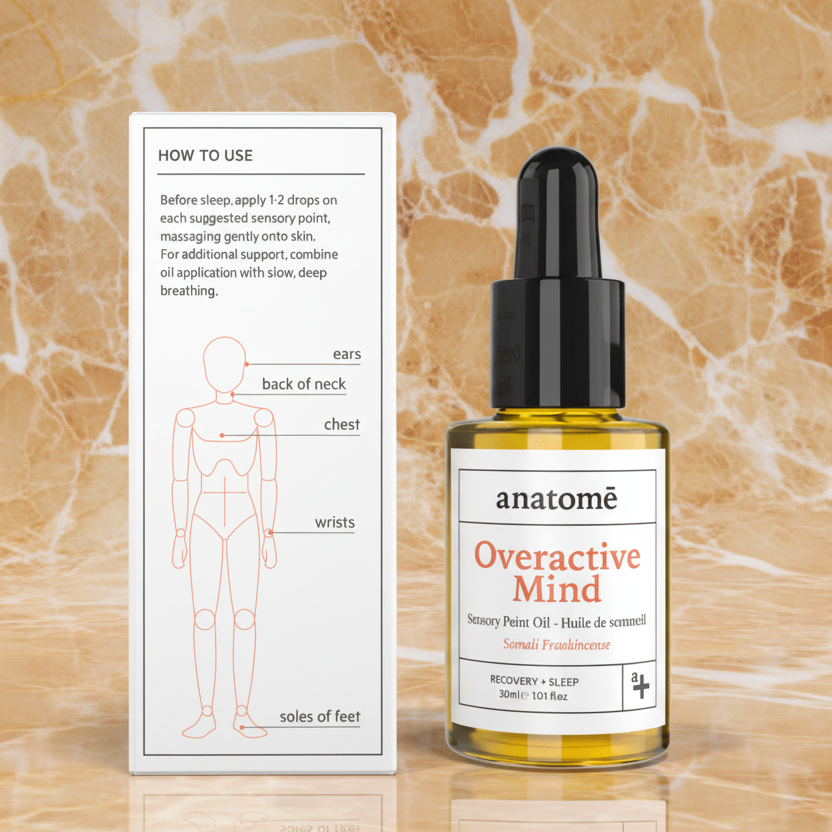
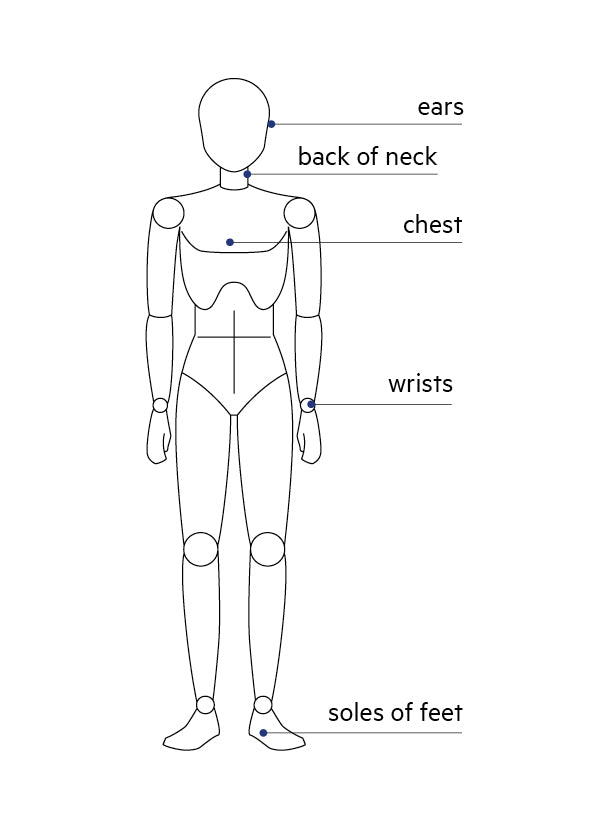
Magnesium can help you feel calmer within hours of your first dose, but consistent daily use over one to two weeks typically delivers noticeable improvements in sleep quality. Some clinical trials track the full benefits over six to eight weeks, particularly for those with significant deficiencies.
The exact timeline depends on several factors: the form you choose, your dosage, how depleted your magnesium stores are, and whether you pair supplementation with good sleep habits. This guide walks you through what to expect at each stage, from the first night through the first few months.
What Does Magnesium Do for Sleep?
Magnesium plays a central role in over 300 enzymatic reactions throughout your body, and many of these directly influence how well you sleep. Understanding what this mineral actually does helps explain why the benefits build gradually rather than appearing overnight.
How Long Does Magnesium Take To Work For Sleep?
The honest answer is that it varies. Some people notice subtle changes within days, while others need several weeks. Here's a realistic breakdown of what typically happens at each stage.
1st Night to 1st Week: Initial Relaxation
Many people report feeling slightly calmer or drowsier within an hour or two of taking magnesium, especially in the evening. This early effect comes from magnesium's interaction with GABA receptors and its muscle-relaxing properties.
Did you know?
A study published in PubMed Central found that participants taking magnesium showed continued improvements through weeks two and three, while the placebo group improved mainly in the first week before plateauing.
During the first week, you might notice:
|
What You May Experience |
What It Means |
|
Mild drowsiness after taking your dose |
Magnesium is beginning to support GABA activity |
|
Slightly easier time unwinding before bed |
Muscle tension and nervous system activity are decreasing |
|
No dramatic change yet |
Your body is still building magnesium stores |
Don't be discouraged if the first few nights feel unremarkable. The real changes typically come with consistency.
1 to 2 Weeks: Noticeable Sleep Improvements
This is when most people start noticing tangible differences. After one to two weeks of daily supplementation, common improvements include falling asleep faster, experiencing fewer nighttime wakings, and waking up feeling more rested.
According to Verywell Health, the one-to-two-week mark represents a typical turning point because your body has had time to replenish depleted magnesium stores and establish more consistent GABA activity.
6 to 8 Weeks: Full Benefits
Clinical trials often run for six to eight weeks to capture the complete picture. A controlled trial in older adults with primary insomnia found that 8 weeks of daily magnesium significantly increased total sleep time and sleep efficiency while reducing the time it took to fall asleep.
Pro Tip: Keep a simple sleep diary during your first eight weeks. Note when you take magnesium, how long it takes you to fall asleep, and how rested you feel upon waking. This helps you identify patterns and determine whether your current approach is working.
How Timing and Dose Affect How Fast Magnesium Works
When and how much you take can influence how quickly you notice results. Getting these details right from the start sets you up for success.
Best Time to Take Magnesium for Sleep
Most experts recommend taking magnesium in the evening, approximately 30 minutes to two hours before bed. This timing allows the mineral to be absorbed and begin interacting with your nervous system before you attempt to sleep.
Taking magnesium too close to bedtime may not give it enough time to work, while taking it too early in the evening might mean the effects begin to wane before you're ready to sleep.
Typical Sleep-Supportive Dosages
Adults generally benefit from 200–400 mg of elemental magnesium daily for sleep support. Starting at the lower end and gradually increasing allows you to assess your tolerance and find the dose that works best for you.
|
Dosage Range |
Best For |
|
200 mg |
Those new to magnesium or with mild sleep concerns |
|
300 mg |
General sleep support and relaxation |
|
400 mg |
Those with greater deficiency or more significant sleep difficulties |
Note: Always check with a healthcare professional before exceeding 400 mg daily, particularly if you have kidney concerns or take other medications.
Why Consistency Matters More Than a Single Dose
A single dose of magnesium won't transform your sleep. The benefits accumulate as your body's magnesium stores are replenished over days and weeks. Skipping doses or taking magnesium sporadically means you're constantly resetting the process rather than building on previous progress.
How Magnesium Affects the Nervous System
Magnesium helps regulate your nervous system by binding to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors in the brain. GABA is your body's primary calming neurotransmitter, responsible for quieting neural activity and preparing you for rest. When magnesium levels are adequate, GABA functions more effectively, which promotes relaxation and reduces the mental chatter that keeps many people awake.
This mineral also helps control cortisol, your stress hormone. Elevated cortisol in the evening disrupts your natural sleep-wake cycle and makes it harder to wind down. Magnesium supports healthy cortisol regulation, creating a more favourable internal environment for sleep.
Magnesium, Melatonin, and Your Sleep-Wake Cycle
Your body produces melatonin to signal that it's time to sleep, and magnesium plays a supporting role in this process. Research from the Sleep Foundation indicates that magnesium helps regulate melatonin production and may enhance its effectiveness. This relationship partly explains why magnesium supplementation often improves both the ease of falling asleep and overall sleep quality.
Signs You May Be Low in Magnesium
Many adults don't get enough magnesium through diet alone. Common signs of insufficiency include:
- Muscle cramps or restless legs at night
- Difficulty falling asleep despite feeling tired
- Waking frequently throughout the night
- Feeling unrested even after adequate sleep hours
- Increased sensitivity to stress
If several of these sound familiar, addressing your magnesium intake might produce more noticeable results than for someone with already-optimal levels.
Searching for a sleep supplement that combines magnesium with complementary botanicals?
Anatomē's Magnesium Reset, Relax + Sleep formula pairs highly absorbable Magnesium Bisglycinate with L-Tryptophan to support your body's natural wind-down process.
Does the Type of Magnesium Change How Fast It Works?
Not all magnesium supplements are created equal. The form you choose affects absorption, tolerability, and how quickly you might notice sleep benefits.
Common Oral Forms Used for Sleep
-
Magnesium Bisglycinate (Glycinate): This form bonds magnesium to the amino acid glycine, which has its own calming properties. It's highly absorbable, gentle on the stomach, and often considered the best option for sleep support. Many users report feeling calmer within a few days, though consistent improvements typically emerge over one to two weeks.
-
Magnesium Citrate: Well-absorbed and widely available, though it has a mild laxative effect that some people find inconvenient.
-
Magnesium L-Threonate: This newer form crosses the blood-brain barrier more effectively and is specifically researched for cognitive and sleep benefits. Studies show promising results, though it tends to be more expensive.
-
Magnesium Oxide: Poorly absorbed and primarily used for digestive purposes. Not recommended for sleep support.
According to WebMD, magnesium glycinate remains the most popular choice for sleep due to its superior absorption and the additional calming effect of glycine.
Topical Magnesium: Sprays, Lotions, and Bath Soaks
Transdermal magnesium (applied to the skin) offers an alternative for those who experience digestive discomfort with oral supplements. Magnesium sprays, lotions, and bath soaks allow the mineral to absorb through the skin, often producing a localised relaxation effect fairly quickly.
The relaxation from a magnesium-rich bath, for instance, can be felt within 20 to 30 minutes. However, topical methods may not raise systemic magnesium levels as effectively as oral supplementation, so they're often best used alongside a quality supplement rather than as a replacement.
Factors That Influence Your Personal Timeline
Two people can take the same magnesium supplement and experience different timelines. Several variables explain this variation.
Age, Stress Levels, and Lifestyle
Older adults often have lower magnesium absorption rates, which may mean a longer timeline to noticeable benefits. High stress depletes magnesium faster, so those under significant pressure might need more time (or a higher dose) to see results. Lifestyle factors like alcohol consumption, excessive caffeine, and intense exercise all increase magnesium excretion.
Diet and Gut Health
If your diet already includes magnesium-rich foods like dark leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains, you may have a smaller deficiency to correct and might notice benefits sooner. Conversely, gut health issues that impair nutrient absorption can slow your progress.
Medications and Health Conditions
Certain medications, including proton pump inhibitors, diuretics, and some antibiotics, can reduce magnesium absorption or increase excretion. If you're taking any regular medications, discuss magnesium supplementation with your healthcare provider to ensure there are no interactions.
What Results Can You Realistically Expect?
Managing expectations helps you stay consistent long enough to experience real benefits. Here's what the research and user experiences suggest.
Short-Term Effects (Days 1–7)
-
Mild relaxation or drowsiness after your evening dose
-
Possible reduction in muscle tension
-
Subtle sense of calm, though sleep patterns may not change dramatically yet
Medium-Term Changes (Weeks 2–4)
-
Falling asleep becomes easier
-
Fewer wakings during the night
-
Improved sleep quality scores if you're tracking with an app or wearable
-
More consistent energy levels during the day
Research found that oral magnesium shortened sleep onset latency by approximately 17 minutes on average compared to the placebo. Its a meaningful improvement for anyone who typically lies awake staring at the ceiling.
Long-Term Benefits (Weeks 6–8+)
-
Established sleep patterns that feel more natural
-
Better stress resilience during the day
-
Potential improvements in related areas, like mood and muscle recovery
How To Take Magnesium So It Works Faster
While you can't rush biology, certain strategies help optimise absorption and create conditions for magnesium to do its best work.
Build Magnesium Into a Calming Bedtime Routine
Taking your supplement at the same time each evening, as part of a consistent routine, reinforces your body's sleep signals. Pair it with other calming activities: dimming the lights, putting away screens, or practising a few minutes of gentle stretching.
Combine With Other Sleep-Supportive Habits
Magnesium works best alongside good sleep hygiene. Keep your bedroom cool, dark, and quiet. Avoid caffeine after midday. Limit alcohol, which disrupts sleep architecture even if it initially makes you drowsy.
Pro Tip:
Layer your approach. A magnesium supplement addresses internal relaxation, while external cues like calming scents signal to your brain that sleep is approaching. This combination often produces faster results than either approach alone.
If you’re in search, anatomē's Somali Frankincense Reed Diffuser fills your space with grounding aromatics that complement your evening wind-down routine. Also, no effort is required once the reeds are placed.
Track Your Sleep to Measure Progress
Use a simple sleep diary or a wearable device to monitor changes over time. Tracking metrics like time to fall asleep, number of night wakings, and morning energy levels helps you objectively assess whether magnesium is making a difference, and whether you might benefit from adjusting your dose or timing.
Safety, Side Effects, and When Magnesium Might Not Work
Magnesium is generally safe for most adults, but awareness of potential issues helps you use it wisely.
Common Side Effects and How to Reduce Them
The most common side effect is digestive upset, particularly with forms like magnesium citrate or oxide. Symptoms may include loose stools, cramping, or nausea. Choosing a gentler form like magnesium bisglycinate typically reduces these issues.
Starting with a lower dose and gradually increasing also minimises digestive discomfort. Taking magnesium with food can further improve tolerability.
Who Should Be Cautious
Individuals with kidney disease should consult a doctor before supplementing, as the kidneys regulate magnesium excretion. Those taking certain heart medications, antibiotics, or blood pressure drugs should also seek professional guidance due to potential interactions.
When to Reassess Your Approach
If you've taken magnesium consistently for six to eight weeks without meaningful improvement, consider:
-
Trying a different form (switching from citrate to glycinate, for example)
-
Adjusting your dose within safe ranges
-
Evaluating other factors affecting your sleep (stress, screen habits, caffeine intake)
-
Speaking with a healthcare professional to rule out underlying sleep disorders
Takeaway
Magnesium isn't a quick fix, but it's one of the most evidence-backed natural approaches to better sleep. Most people begin feeling subtle relaxation within days and notice meaningful improvements within one to two weeks of consistent use. For the full benefits, such as deeper sleep, easier mornings, and better stress resilience, plan on six to eight weeks of daily supplementation.
The key is patience and consistency. Choose a highly absorbable form, take it at the right time, and pair it with supportive habits that signal to your body that rest is coming.
Want to give your sleep routine a considered upgrade?
anatomē combines science-backed ingredients with botanical expertise to support your body's natural wind-down process. From supplements formulated with highly absorbable magnesium to sleep oils crafted with up to 22 botanical extracts, everything is designed in London to help you build a restful evening ritual that works from the inside out.
Important FAQs
Q1. How long does it usually take for magnesium to work for sleep?
Magnesium typically promotes mild relaxation within hours but requires one to two weeks of consistent daily use for noticeable sleep improvements. Clinical studies often track benefits over six to eight weeks for the full effect.
Q2. Can magnesium help you sleep better the first night?
Yes, but some people feel a subtle calming effect within the first dose, though dramatic sleep improvements rarely occur overnight. Benefits build gradually as your body replenishes its magnesium stores over days and weeks.
Q3. How long should I try magnesium before deciding if it helps my sleep?
Give magnesium at least three to six weeks of consistent use before evaluating results. Many people need this time for levels to build sufficiently and for sleep patterns to stabilise noticeably.
Q4. Does magnesium glycinate work faster for sleep than other forms?
Magnesium glycinate is highly absorbable and often produces calming effects within hours to days. However, consistent sleep improvements still typically require one to two weeks of regular use, similar to other well-absorbed forms.
Q5. When should I take magnesium so it works best for sleep?
Take magnesium 30 minutes to two hours before bed for optimal results. This timing allows absorption and gives the mineral time to support relaxation before you attempt to fall asleep.
Q6. What should I do if magnesium hasn't improved my sleep after a few weeks?
Review your dose, form, and consistency first. If everything checks out, optimise your overall sleep habits and consult a healthcare professional to investigate other potential causes of poor sleep.